Competitive Strategy
Static efficiency in mature products may be good for consumers in the short run, but dynamic efficiency in innovative products is what drives the economy and elevates consumer welfare in the long run.
The main purpose of competition among firms is to gain market share. But depending on whether the competition is price-based or innovation-based, the economic implications are very different.
Price-based competition usually involves mature products in a saturated market.
Since there are no new features to attract customers, the only way to gain or maintain market share is to undercut or match the price of competitors. The number of competitors depends on the capital requirement. When the capital requirement is small, there are a lot of small firms (perfect competition). And when the capital requirement is big, there are a few large firms (oligopoly).
When price-based competition is accompanied by single-pricing, most of the economic surplus1 goes to consumers as consumer surplus. The zero-profit firms have little resources to innovate or to maintain service quality. Surprisingly, this state of market entropy is regarded as the model of market efficiency in conventional economic theory because price of the last unit sold is close to or equal to marginal cost.
But this kind of market efficiency is at best static. The economy will stagnate if the market trades only mature products. A dynamic economy requires innovative products that change the competitive landscape. Innovation-based product competition introduces dynamic market efficiency.
Innovative products command premium prices for early adopters and capture most of the economic surplus in the form of profit. But prices will be lowered successively over the product cycle to attract more customers with less urgent needs as most of the R & D costs have been paid for by the early adopters. By practicing such longitudinal price discrimination, the successful firm can use the captured economic surplus to improve the products and come up with additional innovative products. Such innovations may be encouraged by temporary patent protection to slow down copycats.
Some major innovations may destroy or marginalize entire categories of old products. But because old needs are better satisfied and latent needs are now satisfied by innovative products, consumer welfare as a whole is improved. To decry the temporary monopoly conferred on innovative products as statically inefficient is to deny the dynamic role played by innovative products.
As the innovative products mature, entry of competitors will usher in a period of price-based competition where most of the economic surplus will be shared with the consumers.
Within innovation-based competition, there is a whole range of strategies to prolong the dominance of the innovative products. For example, there is the fight for standards and brand dominance, the lock-in effect of networked products, and the extension of market dominance in one product to complementary products, and the gradual introduction of upgrade features to already acceptable products, etc.
Notes:
- Economic surplus is the difference between the reservation price (highest price one is willing to pay) and the marginal cost of a good.
Glossary:
- consumer surplusConsumer surplus is the gap between what buyers are willing to pay and what they actually pay. Consumer surplus is highest when sellers' economic profit is zero and is zero when sellers can practice perfect price discrimination (i.e., selling each unit at buyer's reservation price). See also "economic surplus."
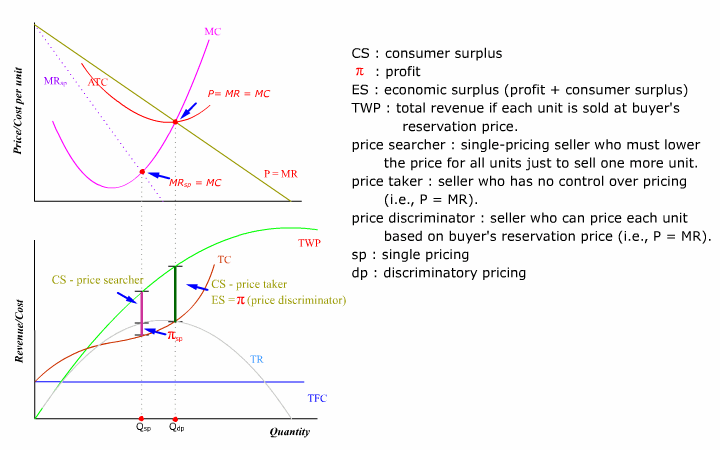
- economic surplusMarginal economic surplus is the difference between the reservation price (highest price one is willing to pay) and the marginal cost of a good. Total economic surplus is the sum of total consumer surplus and total economic profit. Total economic surplus is also the difference between TWP and TC. Under perfect price discrimination, economic surplus is maximized when profit is maximized. But under single pricing, maximizing profit does not generally maximize economic surplus.

- efficiencyA state when the marginal social benefit of an activity is equal to its marginal social cost.
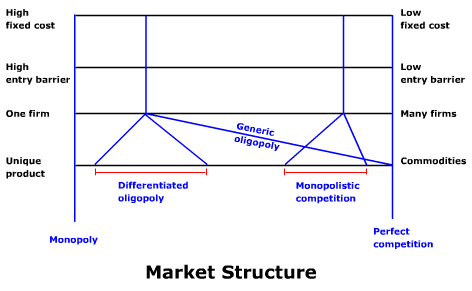
- oligopolyAn industry dominated by a few large firms. A generic oligopoly sells homogeneous products. A differentiated oligopoly sells differentiated products.
- patentA temporary but exclusive right given by the government to an inventor to profit from the invention in exchange for sharing the information with the public.
- perfect competitionA market structure where barriers to entry and exit are absent. Sellers have no individual pricing power but must sell at the prevailing market price. At equilibrium, sellers just cover all costs and earn zero economic profit.
- price discriminationCharging different customers at or close to their reservation prices for the same goods. Price discrimination is intended to increase sellers' economic profit and reduce consumer surplus.
- product competitionCompeting for business on the basis of innovative products.
- short runA time horizon that is too short for the fixed input to be adjusted or for all costs to be variable.
- single pricingCharging the same price to all buyers regardless of their reservation prices in one pricing period. Those buyers whose reservation prices are higher than the single price will gain consumer surplus. All sellers who are not practicing perfect price discrimination are single pricers to various degrees. However, price takers individually have no power to change the single price. Only price searchers can adjust their single prices to take advantage of varying demand elasticities over prices.
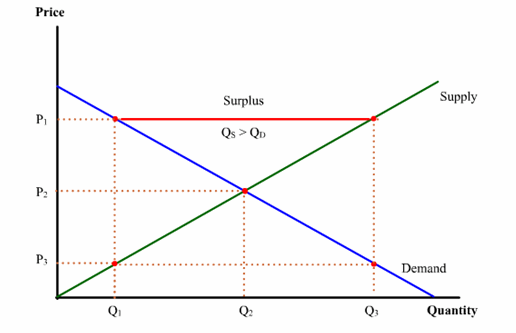
- surplusThe excess of quantity supplied over quantity demanded at a given price. Also known as excess supply.
Topics:
Keywords
brand dominance, consumer surplus, dynamic efficiency, economic surplus, innovative products, lock-in effect, market structure, mature products, monopoly, network product, oligopoly, patents, perfect competition, price discrimination, single pricing, standards, static efficiency
