Complements and Substitutes
Complements and substitutes illustrate the difference between changes in quantity demanded vs changes in demand.
Glossary:
complementary goods
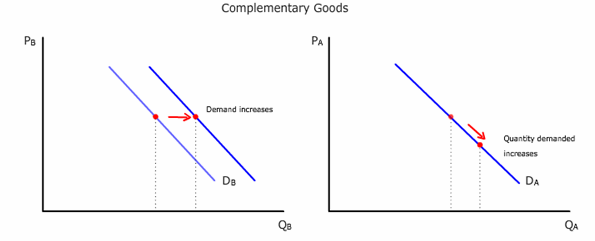
Two goods (A and B) are complementary when an increase in quantity demanded for A due to a price decrease of A leads to an increase in demand for B and vice versa. For example, when airfare to Hawaii goes down, more tickets are sold. That is, quantity demanded increases. When more tickets are sold, more hotel rooms at Hawaii are needed even though hotel rates have not changed. That is, demand has increased. (Note: Professor Richard Evans provided this example.)
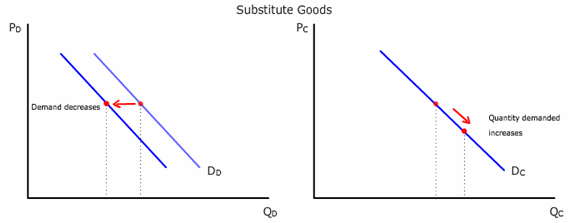
substitutes
Two goods (A and B) are substitutes when an increase in quantity demanded for A due to a price decrease of A leads to a decrease in demand for B and vice versa.