External Benefit and External Cost (transcript)
The existence of external cost and external benefit leads to misallocation of resources.
Introduction
When an action generates benefit for which the benefactor has no right to collect payment and the beneficiary has no obligation to pay, an external benefit arises.
When an action generates adverse spillovers for which the impactor has no obligation to pay and from which impactee has no right to claim damages, an external cost arises.
The existence of external benefit and external cost leads to misallocation of resources.
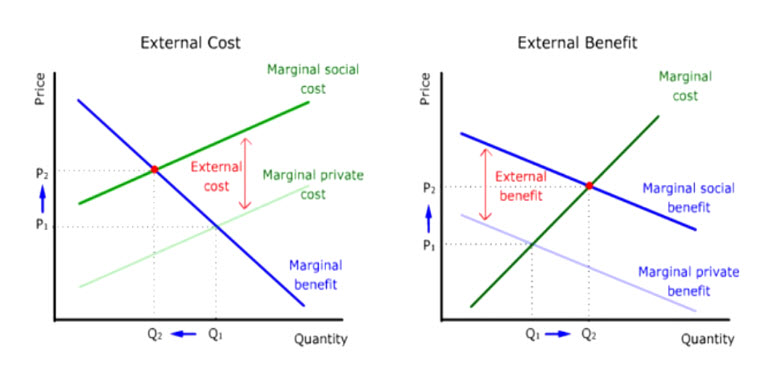
External cost
For example, when drivers are not liable for the health damage of car exhaust, drivers will equate only marginal private cost with marginal benefit. But if drivers are forced to pay for the health damage of car exhaust, their marginal cost will go up by the amount of the external cost.
In other words, drivers are forced to equate marginal social cost with marginal benefit.
As a result, quantity demanded will go down and price of gasoline will go up if the marginal benefit stays the same.
External benefit
On the other hand, if inventions are not patentable to keep out imitators, licensees of inventions will equate only marginal private benefit with marginal cost. But if licensees are protected against imitators, their marginal benefit will go up by the amount of the external benefits.
In other words, licensees can now afford to equate marginal social benefit with marginal cost.
As a result, quantity supplied will go up and price for inventions will also go up if the marginal cost stays the same.
Side-by-side comparison
Here is a side-by-side comparison of the effects on price and quantity demanded when external cost and external benefit are internalized.
When external cost or external benefit is present, the market price for the activity that generates external cost or external benefit is too low to be efficient.
When these externalities are internalized, price will go up in both cases. But the quantity demanded will go down when external cost is internalized. And the quantity supplied will go up when external benefit is internalized.
Summary
• External cost and external benefit exist because some property rights have not been clearly defined.
• When external cost is present, the activity that generates external cost is priced too low and the quantity demanded is too high to be efficient.
• When external cost is internalized, price will go up and quantity demanded will go down if demand stays the same.
• When external benefit is present, the activity that generates external benefit is priced too low and the quantity demanded is too low to be efficient.
• When external benefit is internalized, price will go up and quantity supplied will go up if supply stays the same.
Coase Theorem
Externalities can be eliminated when all property rights are clearly defined and transaction costs among right holders are zero.
Topics:
Keywords
Coase Theorem, external benefit, external cost, externality, internalization, resource allocation
