Free-Market Solutions
Free-market solutions can minimize cost and rent dissipation of market interventions and regulation.
Most regulations resort to across-the-board prohibitions that unnecessarily increase the total cost of compliance. Or scarce resources are allocated politically rather than through open bidding leading to rent dissipation. The ability of the market to minimize cost or reduce rent dissipation is thereby under-utilized.
We will look at some ingenious free-market approaches to intervene or regulate that will achieve both macro-stability and micro-flexibility. These approaches are as follows:
Some of these approaches are already adopted while others are blueprints for possible adoption.
Glossary:
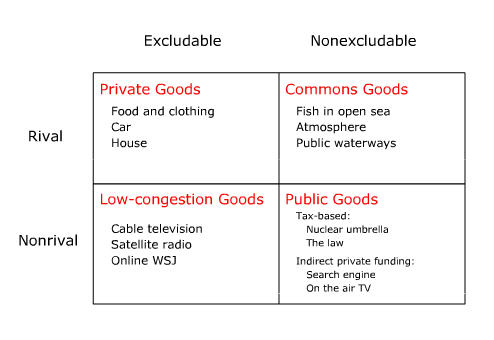
- commons goodA commons good is one that is available to all potential users but subject to congestion. A popular public beach is a commons good prone to traffic congestion in summer.
- external benefitsFree benefits conferred on innocent third parties due to unassigned or poorly assigned property rights or when the cost exceeds the benefit of exercising properly assigned rights. Also known as positive externality.
- property rightThe control over the use or transfer of a resource. Property right is conducive to efficient use of scarce resources as owners have an incentive to maximize their long-term returns.
- regulationGovernment actions to temper the adverse effects of uncontrolled market activities.
- rent dissipationEconomic rent is dissipated when it is neither available to rent seekers nor those who create the rent by restricting economic activities desired by rent seekers.
Topics:
Keywords
cost, free market solutions, intervention, macro-stability, market, micro-flexibility, regulation, rent dissipation
